As India is positioned near several powerful trade nations such as China, Bangladesh, and Japan, being an exporting country becomes a significant potential with a lot of rivalries. All export rules must be strategically and legally followed to make exporting a feasible and simple operation.
India has one of the world’s largest economies; imports and exports of goods and services account for a significant portion of its GDP. The Foreign Trade (Development & Regulation) Act of 1992 and India’s Export Import (EXIM) Policy govern the import and export of products and services in India.
Understanding the parties and the various stages of the export process is critical. Some websites give article information, but they are scattered and fearful of some detail, so in this article, we will try to provide a thorough and simple approach for import export business in India.
The following is a list of import and export processes that you should be familiar with.
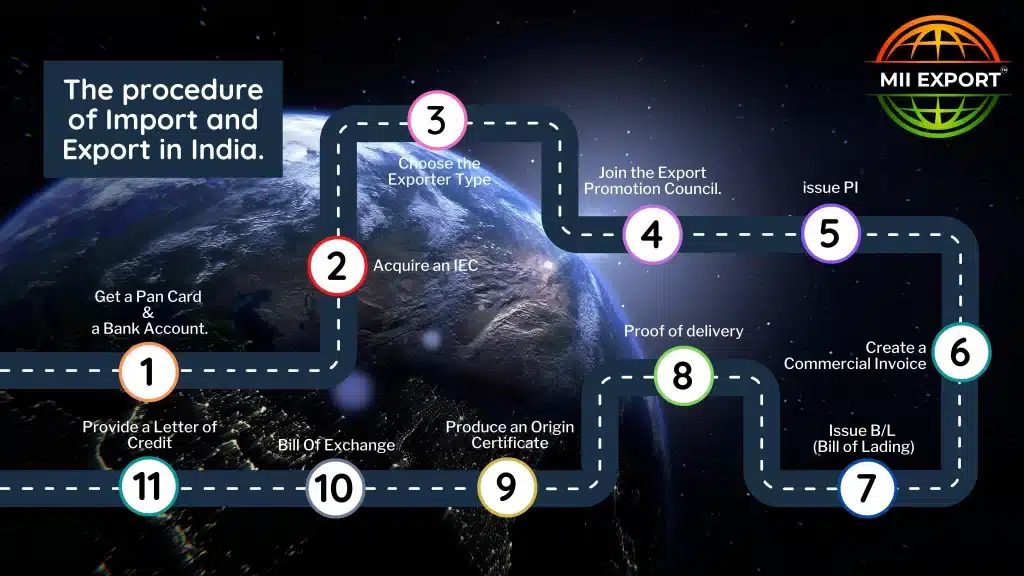
Import and Export process steps :
- Get a Pan Card and a Bank Account
Establishing a bank account and, from there, acquiring a PAN Card is a fundamental step towards becoming a businessman or importer-exporter. - Acquire an IEC
The Indian government has given the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) the authority to issue a ten-digit number to any individual or corporate organization. It is known as the Import Export Code, and it is required for any international operation. One can apply for IEC by giving the entity’s PAN Card and bank account information. - Choose the Exporter Type
Exporters are classified into two types: manufacturer exporters and exporter merchants. A producer exporter is a person or institution that creates items and sells them overseas, whereas a merchant exporter is a businessman that does not manufacture goods but sells them abroad. - Join The Export Promotion Council
It is necessary to register with the Export Promotion Council or a commodities board in India. It allows you to do business safely while also reaping some of the benefits of exporting. - Issue PI (proforma invoice)
The exporter issues a PI (proforma invoice) to the importer. - Create a Commercial Invoice
A commercial invoice is an invoice sent by the exporter to the importer that serves as proof of transaction. - Issue B/L (Bill of Lading)
A bill of lading is a legal document the port authorities require for clearance. - Proof of Delivery
In most cases, the importer pays for the shipping and collects the products, thus the exporter must submit shipment evidence to the importer so that he may take receipt of the items from the port. - Produce an Origin Certificate
The issuance of a certificate of origin is required for customs clearance. - Bill of Exchange
It is a written document that is issued to clear payment terms. - Provide a Letter of Credit
Letters of credit must be issued in both local and foreign commercial operations.
All of the following import and export procedures must be followed while conducting business. Via its internet portal and Chamber of Commerce, the government is always available to assist an individual or company in conducting business.
